 Books can be the best Christmas gifts, at least in my humble opinion. I have already finished one novel that I received for Christmas, Singapore Exile Murders by F. van Wyck Mason. Written, published, and set in 1939, the novel incorporates the responses of Europeans and Americans in southeast Asia to the global events leading up to World War II, making it an intriguing historical artifact based on one person’s imaginings. As a piece of data, the language in the novel surprised me at points, including the off-hand use of terms for African-Americans and Chinese that would be considered offensive today.
Books can be the best Christmas gifts, at least in my humble opinion. I have already finished one novel that I received for Christmas, Singapore Exile Murders by F. van Wyck Mason. Written, published, and set in 1939, the novel incorporates the responses of Europeans and Americans in southeast Asia to the global events leading up to World War II, making it an intriguing historical artifact based on one person’s imaginings. As a piece of data, the language in the novel surprised me at points, including the off-hand use of terms for African-Americans and Chinese that would be considered offensive today.
Beyond illustrating how what is considered acceptable has shifted in the past 75 years, these problematic terms (by our standards) also illustrate the ways everyday language reinforces, even makes appear normal, social hierarchies. The ways that Europeans and European-American characters use these terms in casual speech places African-Americans (who do not appear as characters in the novel) in the position of menial, hard laborers and Chinese (who are primarily servants, rickshaw pullers, and the like) as clearly inferior. The condescending labels thus socialize people into particular positions of inferiority and superiority by making the hierarchy appear natural, simply the way things are. Continue reading “PC Power”

 A culture is not a costume. That sentiment has become a common theme on social media and student newspapers (
A culture is not a costume. That sentiment has become a common theme on social media and student newspapers ( Darth Vader vs. Luke Skywalker, Sauron vs. Gandalf, Voldemort vs. Harry Potter. Stories are full of good and bad characters, sometimes complicated with the redemption of a character like Darth Vader, but what does it take to maintain such a stark division between good and evil?
Darth Vader vs. Luke Skywalker, Sauron vs. Gandalf, Voldemort vs. Harry Potter. Stories are full of good and bad characters, sometimes complicated with the redemption of a character like Darth Vader, but what does it take to maintain such a stark division between good and evil?

 Bruce Lincoln, Holy Terrors: Thinking About Religion After 9/11 (Chicago: University of Chicago Press, 2003)
Bruce Lincoln, Holy Terrors: Thinking About Religion After 9/11 (Chicago: University of Chicago Press, 2003) Read
Read 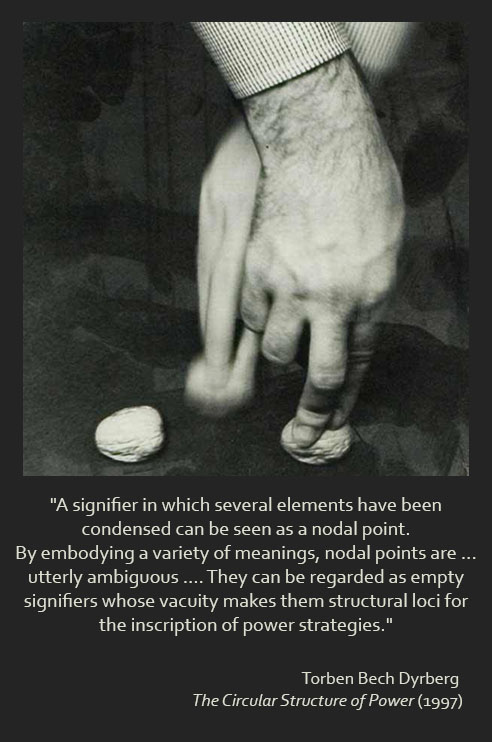
 For
For  Read
Read  Read
Read